- Topvisor Help Center /
- Updates Scanner
Updates Scanner. How to track volatility in search results
A search engine has a pool of documents (URL pages) it analyzes. It picks some of them to display the most relevant results to a user in a specific order. In other words, it generates a search engine results page (SERP). The database of these documents is called the search engine index, and the pages within it are referred to as indexed. If a page is indexed, it means it participates in ranking and, theoretically, can appear in the Top if a search engine deems it relevant to the user's intent.
Every day, millions of new pages are published on the internet, and search engines must index, analyze, and display them in response to users' keyword phrases — provided the pages meet the search intent. As a result, the search index is continuously updated, making search results highly dynamic. The degree of changes in search results is referred to as "SERP volatility". You can monitor search index updates and volatility intensity using Updates scanner.
How to go to Updates Scanner
To go to Updates Scanner click in the header. Go to Updates Scanner →

How Updates Scanner works
Updates Scanner collects the Top search results every day for a selected pool of keywords across popular topics and compares the results to previous checks. Based on these comparisons, it calculates the degree of ranking changes using a 10‑point scale. The level of volatility is visually represented in the Update Calendar using cell colors and weather icons:
- Up to 4 points – White cell;
- 4‑6 points – Green cell;
- 6‑8 points – Yellow cell;
- 8‑10 points – Red cell.
Additionally, the Update Calendar includes checkmarks indicating whether a search engine update occurred in Yandex:
- — text updates (search index updates). signify that the search engine index has been refreshed, with 10 to 100 million new documents indexed. If more than 100 million documents were added, there will be
- — search results updates.
Is there a specific SERP volatility score at which an update is detected?
Why does an earlier text index appear for a later update date? For example, on 01.05, an index for 26.04 was released, and on 03.05, one for 17.04.
If the text update on 01.05 shows an index dated 26.04, it means that by 01.05, pages created up to and including 26.04 were detected in the index. However, this doesn't mean that Yandex's index won’t include pages created after 26.04 — it simply indicates that the majority of pages created after 26.04 are not yet indexed. This should be taken into account when planning your SEO strategy.
The same applies to the 03.05 update: it reflects the inclusion of pages created up to 17.04. It’s also important to consider the strength of the update, represented by yellow and red checkmarks:
- A yellow checkmark indicates a minor index update, during which 10 to 100 million documents were indexed;
- A red checkmark signifies a major index update, with over 100 million documents indexed.
A yellow checkmark represents a relatively weak update. Even though millions of documents are added, this is relatively minor for the search engine. In practice, this means that only a small portion of documents was indexed in the update on May 1, another small portion in the update on May 3, and so on. For example, if numerous documents are indexed on May 5 (with a red checkmark), documents not included in the May 1 and May 3 updates may be indexed on May 5.
It’s also important to analyze how index updates impact rankings and whether Updates Scanner detected a ranking update. There may be cases where Scanner does not record changes in rankings. A ranking update is marked with a green checkmark, indicating changes not only in the number of indexed documents but also in search rankings and the Top websites in the results. To detect updates, Update Scanner crawler collects Top results for a keyword pool every day and compares them to previous results. If the rankings shift beyond a certain threshold, an update is recorded.
UI Map
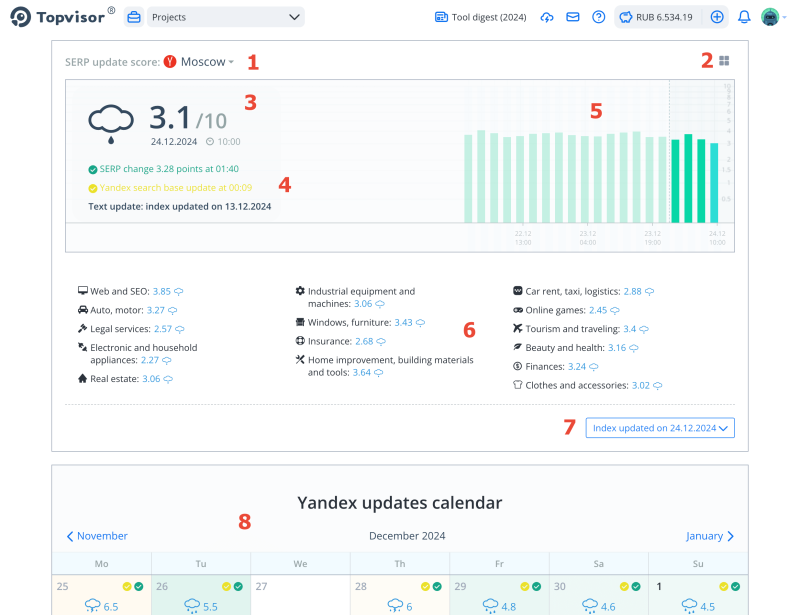
- Search engine and location.
- Filter by topics.
- SERP Volatility, date, and time of the latest check in Updates Scanner.
- Information about updates.
- Hourly SERP volatility chart. Hover over the column to see the date, time, and volatility intensity.
- SERP volatility by topics. Click on a topic to apply a filter.
- Show/hide the table with the index.
- Update calendar. Click on a date to select it.
How volatility differ in Yandex and Google
In Google, the search index is updated continuously and evenly, resulting in a constant but mild SERP volatility. There’s no concept of "updates" as in Yandex. Yandex, on the other hand, adds documents to its search index in "batches" resulting in bursts of millions of new documents being indexed simultaneously. These updates are called text updates, and they can be tracked in Updates Scanner.
Why do updates usually happen at night?
How SERP volatility affect website rankings
Volatility indicates that the Top search results are fluctuating and rankings are unstable. As a result, websites might experience significant ranking changes. We don’t recommend checking rankings immediately after a period of SERP volatility because rank tracking tools record rankings at the exact moment of the check. If the tool captures a session during significant rank fluctuations, this will be reflected in the data. Typically, rankings stabilize some time after the volatility, with websites either settling into new ranks or returning to their previous ones. We recommend checking rankings only after the volatility has passed and the rankings have stabilized.
Learn more about how SERP volatility affect website rankings →
If it’s crucial for you to know whether your website’s ranking has changed after a Yandex update, set up automatic checks in your project. You can specify whether to check rankings immediately after an update or wait a few hours. Note that rankings will be checked not only in Yandex, but also in all search engines added to your project.